To see videos explaining how to complete each task, view:
Task #1: https://youtu.be/bTrqdHvAr_8
Task #2: https://youtu.be/ANGO1MelUN4
Task #3: https://youtu.be/fLty4SCoqfI
Task #4: https://youtu.be/mJL3Bswbs5w
Launch SSMS and use the New Query command. At the top of the query window, type /* Your Name, press the enter key and type Task #1 */ Placing text withing /* and */ creates a comment that will be ignored when you run the query.
a) Enter the following query:
USE AP;
SELECT * FROM
Invoices;
b) Execute the query using the execute command button (or press F5)
c) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
Example:
/* Lisa Balbach
Task #1
USE AP;
SELECT * FROM
Invoices; */
a) Enter the query below the closing comment.
b) Run the query to make sure it works
c) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
Example:
/* Lisa Balbach
Task #1
USE AP;
SELECT * FROM
Invoices;
USE AP;
SELECT InvoiceID, InvoiceDate, InvoiceTotal
FROM Invoices
ORDER BY InvoiceTotal DESC;*/
a) Copy the previous query by dragging over the query and pressing CTL + C or the copy button on the toolbar.
b) Paste the query below the closing comment
c) Modify the SELECT statement to the following:
SELECT TOP 5 PERCENT InvoiceID, InvoiceDate, InvoiceTotal
d) Run the query to make sure it works
e) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
a) Copy the previous query by dragging over the query and pressing CTL + C or the copy button on the toolbar.
b) Paste the query below the closing comment
c) Change the SELECT clause to the following:
SELECT InvoiceID, InvoiceTotal
d) Insert PaymentTotal + CreditTotal AS 'Total Credits' after InvoiceTotal (so, your select should have InvoiceID, InvoiceTotal, PaymentTotal + CreditTotal AS 'Total Credits' for the columns)
e) Add a WHERE clause to filter InvoiceID to display only ID 17. NOTE: This goes between the FROM and ORDER BY clauses
WHERE InvoiceID = 17
f) Run the query
g) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
h) Save the queries using the Save command button. Name the query chapter3-textbook-assignment (SSMS will put a .sql extension on the end of the name). Make sure you save the file to a jump drive or a directory on your computer that you can easily find (if you are on-campus, please save to your Q drive so you don't lose your work!)
a) Enter Task #2 below the existing queries and move the closing comment symbol */ after the text
b) Create a SELECT query that eliminates duplicates and displays VendorCity. You will need to use the AP database and the Vendors table.
c) The tricky part of the query is the WHERE clause. You will need to use the LIKE operator. Because the first 3 letters are specified and the rest don't matter, you will need to use the %
WHERE VendorCity LIKE 'SAN%'
d) Run the query to make sure it works (you should see 4 cities listed)
e) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
f) Save your changes.
a) Create a SELECT query that displays VendorContactFName and VendorContactLName from the Vendors table in the AP database.
b) For the WHERE clause, you will need to use a LIKE operator. To indicate that it should look for different letters in a specific position, you need to put the letters in brackets.
WHERE VendorContactLName LIKE 'DAMI[EO]N'
c) Run the query to make sure it works
d) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
e) Save your changes.
a) Create a SELECT query that displays VendorName and VendorZipCode from the Vendors table in the AP database.
b) For the WHERE clause, you will need to use a LIKE operator. To indicate that it should look for different numbers between the 9 and 1, enter an underscore (_) for each number
WHERE VendorZipCode LIKE '9___1'
c) Run the query to make sure it works (all zipcodes should begin with a 9 and end with a 1)
d) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
e) Save your changes.
a) Create a SELECT query that displays everything from the Vendors table in the AP database.
b) For the WHERE clause, you will need only show rows where VendorAddress2 IS NOT NULL
WHERE VendorAddress2 IS NOT NULL
c) Run the query to make sure it works
d) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
e) Save your changes.
USE AP;
SELECT InvoiceID, InvoiceDate, InvoiceTotal
FROM Invoices
ORDER BY InvoiceDate;
a) Enter Task #3 below the existing queries and move the closing comment symbol */ after the text
b) Copy and paste the query shown above letter a)
c) Add the following WHERE clause between the FROM and ORDER BY clauses
WHERE InvoiceDate BETWEEN '2020-01-01' AND '2020-01-31'
NOTE: When you enter dates, they are placed in single quotes
d) Run the query
e) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
f) Save your changes
A few things to note here:
1) Balance Due is a calculated column with a column alias
2) You cannot use a column alias in a WHERE clause
3) You CAN use a column alias in an ORDER BY clause
a) Copy and paste the query you just created
b) Add the balance due calculation to the end of the select column list
SELECT InvoiceID, InvoiceDate, InvoiceTotal, InvoiceTotal-PaymentTotal-CreditTotal AS 'Balance Due'
c) Change the WHERE clause to use the calculation instead of the InvoiceDate
WHERE InvoiceTotal-PaymentTotal-CreditTotal > 0
d) Change the ORDER BY clause to use 'Balance Due' instead of InvoiceDate
ORDER BY 'Balance Due' DESC;
e) Run the query
f) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
g) Save your changes
A few things to note here:
1) You cannot use a column alias in a WHERE clause
2) When there are multiple criteria in a WHERE clause, you can use parenthesis to change the order of evaluation. Since the boss only wants InvoiceTotal or Balance Due, they will need to be in parenthesis with the OR operator between them
a) Copy and paste the last query
b) Modify the WHERE clause to the following:
WHERE InvoiceDate > '2020-01-01' AND (InvoiceTotal > 500 OR InvoiceTotal - PaymentTotal - CreditTotal > 0)
c) Run the query. If you look at the results, you will notice that when Balance Due is 0, the InvoiceTotal is > 500. when the InvoiceTotal is < 500, the Balance Due is > 0
d) Move the closing comment symbol */ to the end of the query which will comment out the query
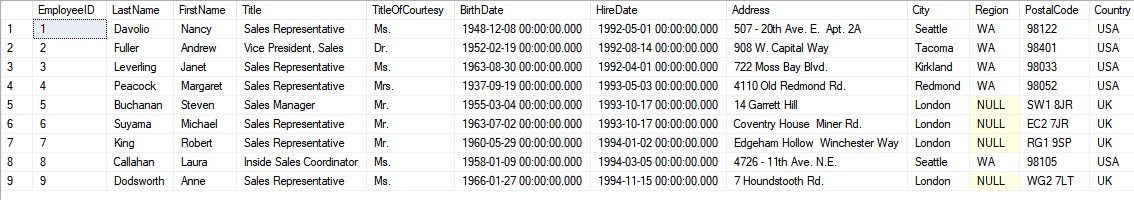
The employees table contains the following data:

To display the rows our boss would like to see, we are going to use the criteria
City <> 'Seattle' AND Title <> 'Sales Representative'
In normal programming, this type of filter would result in all rows displaying except the first row (so 8 rows would display). In SQL, things are procesesed a little differently. It will process the first condition and apply it to all rows, removing any row with a city = Seattle. Then, it will process all titles, removing any row with a Title = Sales Representative. The result is 2 rows displaying.
a) Start by specifying the Northwind database:
USE Northwind;
b) Select all columns in the Employees table:
SELECT * FROM Employees
c) Add the selection criteria City <> 'Seattle' AND Title <> 'Sales Representative' using a where clause.
d) Run the query (you should see rows for employees 2 and 5 display)
e) Save your changes and upload the chapter3-textbook-assignment.sql file to the dropbox