To see a video demonstration for task #1, view: https://youtu.be/ZGrxX6kMnes
To see a video demonstration for task #2, view: https://youtu.be/iyoJjlUFMnY
To see a video demonstration for task #3, view: https://youtu.be/CvtK6rC4HnQ
To see a video demonstration for task #4, SQL CASE function view: https://youtu.be/A-m90Yx1wVA
To see a video demonstration for task #4, SQL IIF function view: https://youtu.be/3J7PI7DkXcI
To see a video demonstration for task #4, SQL CHOOSE function view: https://youtu.be/v61o89O5S2Y
To see a video demonstration for task #4, SQL COALESCE function view: https://youtu.be/DgayrI6CBHo
To see a video demonstration for task #4, SQL ISNULL and GROUPING with CASE functions view: https://youtu.be/UXrGKAIYZBE

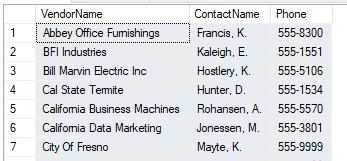
Contact name is a combination of LastName and FirstName and Phone doesn't display the area code. The results are filtered by area code 559 and everything is sorted by vendor name
1 Add a comment that says Task #1
2 To get the required format, we will need to concatenate VendorContactLName, a comma and the first initial of VendorContactFname followed by a period. This should be given an alias of ContactName. We also need the phone number without the area code.
a) For the name, we can use LEFT(VendorContactFName,1) to get the first initial
b) For concatenation, we can use the + sign (we could also use the CONCAT function, but the + sign is faster and easier).
c) For the phone#, we can use the RIGHT function with VendorPhone and retrieve 8 digits if we are concerned that there are spaces at the end, we could use RTRIM, followed by RIGHT: RIGHT(RTRIM(vendorPhone),8)
d) To filter by the area code requires using SUBSTRING(VendorPhone,2,3) and setting that equal to 559. NOTE: position 1 contains the ( which is why we start at 2 to retrieve the 3 digits (we are omitting parenthesis)
e) Here’s the full command:
3 Execute the query, comment it out and save the file as
Chapter9-Textbook-Assignment.sql
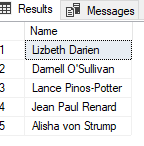
1. When this problem occurs, you can use the CHARINDEX function to locate the characters that separate the components. Then, you can use the LEFT, RIGHT, SUBSTRING, and LEN functions to extract the individual components
To see how this works, enter the following select statement (we will
separate first and last name)
--BEFORE CHANGES
USE Examples;
SELECT Name
FROM StringSample;
Result Set
Result Set
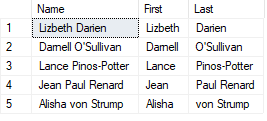
2. After executing both queries, comment them out and save your
changes
1. To generate a random number between 1 and 5, we need to use the following formula:
CEILING(RAND( CHECKSUM( NEWID())) * 5)
Just using RAND( CHECKSUM( NEWID())) by itself, gives a number between 0 and 1. Multiplying by 5 gives us random numbers between 0 and 5, but they have decimal places. To round the values up so they begin with the number 1 and end with a 5, we need to use CEILING
2. Enter the following select statement:
USE Examples;
SELECT *
FROM Investors
WHERE InvestorID
=CEILING(RAND( CHECKSUM( NEWID())) * 5);
Each time you execute the select, a different Investor should display
3. Execute the query 3-4 times and then save your changes. Comment out the query.
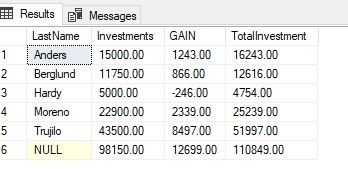
NOTE: ROUND cannot change a float or double value to an integer. If the value is float or double, it will change the decimal places to zero and either round up or round down depending upon what the decimal values were.
5. It is easiest (and less error prone) to enter the code without rounding first and then add the rounding in Enter the following select statement with aggregate functions and the rollup clause
USE Examples;
SELECT LastName, SUM(Investments) AS Investments,
SUM(NetGain) AS GAIN, SUM(Investments+NetGain) AS TotalInvestment
FROM Investors
GROUP BY LastName WITH ROLLUP
6. Excecute the command to make sure it works and then add in rounding as shown below
7. After executing the query, comment it out and save your changes.
Example:
1.
Add a comment of Task #3
2. To create the desired output, we will need to use the MONTH function and the DAY function
Enter the following SELECT:
USE Examples;
Select VendorID,
InvoiceID, MONTH(InvoiceDueDate) AS [MONTH DUE], DAY(InvoiceDueDate) AS
[DAY DUE]
FROM ActiveInvoices;
3. Run the query, save your file and comment out the query.
1. To accomplish this task, we will first run a select to
display everything from the DateSample table so we can see what we are
working with
USE Examples;
SELECT * FROM DateSample;
2. From the data displayed, we can see the StartDate column is the one we need to use the Date Functions with. To get the month, we will use MONTH(StartDate) to get the day, we will use DAY(StartDate) and to get the year, we will use YEAR(StartDate) Since we need to filter the data based on the day, month and year and we dont' want to deal with time settings, we will use the functions and compare them to the values in a WHERE clause
Modify the query to include the WHERE clause shown below:
WHERE MONTH(StartDate) = 10 AND DAY(StartDate) = 28 AND YEAR(StartDate) = 2019;
You should see 1 result displayed that meets our filter criteria
3. Comment out the query and save your changes.
1 = Net due
10 days
2 =Net due 20 days
3 =Net due 30 days
4 =Net due 60
days
5 =Net due 90 days
1. Add a comment of Task #4
2. We need to include the CASE function as one of the columns in the SELECT statement as shown below:
USE AP;
SELECT InvoiceNumber, TermsID,
CASE TermsID
WHEN 1 THEN 'Net due 10 days'
WHEN 2 THEN 'Net
due 20 days'
WHEN 3 THEN 'Net due 30 days'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Net due
60 days'
WHEN 5 THEN 'Net due 90 days'
END AS Terms
FROM
Invoices;
3. Execute the query, save your file and comment out the query
CASE
WHEN DATEDIFF(day,
InvoiceDueDate, GETDATE()) > 30 THEN 'Over 30 days past due'
WHEN
DATEDIFF(day, InvoiceDueDate, GETDATE()) > 0 THEN '1 to 30 days past
due'
ELSE 'Current' END AS Status
In addition to displaying the Status message, we also need to display InvoiceNumber, InvoiceTotal, Invoice Date and InvoiceDueDate
The boss only wants invoices that have a total amount > 0
1. Enter and run the query shown below:
USE
AP;
SELECT InvoiceNumber, InvoiceTotal, InvoiceDate, InvoiceDueDate,
CASE
WHEN DATEDIFF(day, InvoiceDueDate, GETDATE()) > 30 THEN 'Over 30
days past due'
WHEN DATEDIFF(day, InvoiceDueDate, GETDATE()) > 0 THEN
'1 to 30 days past due'
ELSE 'Current' END AS Status
FROM Invoices
WHERE InvoiceTotal - PaymentTotal - CreditTotal > 0;
You will notice that everything is over 30 days past due. To test for 1 to 30 days and Current, we need to add a few rows to the Invoices table using the current date.
2. Comment out the query and insert the following row into the Invoices table:
INSERT INTO Invoices VALUES(10,'10000',GETDATE()-30,5000,200,0,5,GETDATE()-20,GETDATE()-10);
INSERT INTO Invoices VALUES(20,'11000',GETDATE()-20,5000,200,0,5,GETDATE()-10,GETDATE());
INSERT INTO Invoices VALUES(30,'12000',GETDATE(),5000,200,0,5,GETDATE()+30,GETDATE()+30);
INSERT INTO Invoices VALUES(40,'13000',GETDATE(),5000,200,0,5,GETDATE(),GETDATE());
To ensure that we will be able to test current and 1 to 30 days, we are using the GETDATE() function to generate the dates.
3. After inserting the rows, comment out the insert statements by placing two minus signs at the beginning of each row. Then move the closing comment to the end of the previous query and run the query again (see below)
Sample Output:
4. Save all your changes and comment out the code.
Data is in the Examples database, ActiveInvoices table
For the IIF statement, we need to look at CreditTotal>500. In the true position, we need ‘Premier’. In the false position, we need ‘Normal’
1. Enter the following query:
USE Examples;
SELECT VendorID,
IIF(CreditTotal>500,'Premier','Normal') AS CustomerType
FROM
ActiveInvoices;
2. Execute the query, save your changes and comment out the query
To display the red flag, we need to use IIF
IIF(LastYTDPurchases>YTDPurchases,'Red Flag',' ') AS [Need to Contact]
To display the contact name in the format the boss wants requires retrieving the first initial, concatenating with a period and space and then concatenating with the last name:
LEFT(VendorContactFName,1) + '. ' + VendorContactLName AS Contact
To properly display the phone number, we should trim off the spaces (the character column has a width of 50. To trim off spaces on both sides, we need to do the following:
LTRIM(RTRIM(VendorPhone))AS Phone
1. We need to enter the following query:
2. Comment out the code after you execute the query.
1=10 days
2=20 days
3=30 days
4=60 days
5=90
days
The boss only wants to see information where the InvoiceTotal – PaymentTotal- CreditTotal > 0
1. To accomplish this, we need to use the choose function and index into the list using the TermsID
CHOOSE(TermsID, '10 days', '20 days', '30 days', '60 days', '90 days') AS NetDue
2. We need to enter the following select statement:
USE AP;
SELECT InvoiceNumber, InvoiceDate, InvoiceTotal,
CHOOSE(TermsID, '10
days', '20 days', '30 days', '60 days', '90 days') AS NetDue
FROM
Invoices
WHERE InvoiceTotal - PaymentTotal - CreditTotal > 0;
3. Run the query, comment out the query and save your file
1. The actual project number is the last digit in the ProjectNo column. So, we need to retrieve the last digit in the ProjectNo column and use that to index into a choose list with the following information
1=Marketing Call System
2=AP System
3=Warehouse Tracking
4=SalesRep Earnings
5=NA
We will be using RIGHT(ProjectNo,1) as an index into our CHOOSE list
CHOOSE(RIGHT(ProjectNo,1),'Marketing Call System', 'AP System','Warehouse Tracking','Salesrep Earnings','NA') AS ProjectName
The result from the CHOOSE will display as a column in the table.
2. We need to
enter the following select statement:
3. Comment out the code after executing the query.
1 Download wages.txt
2. Copy/paste the text into SSMS and execute it to create a wages table in the Examples database. Comment out the code.
3. To see all the data in the table, enter
USE Examples
SELECT *
FROM Wages;
You should notice we have a lot of null values to work with. Comment out the code.
We can use COALESCE to display the pay for all the employees because the pay will be either hourly, salary or commission.
1. Enter the query below:
USE Examples;
SELECT emp_id, COALESCE(hourly_wage*40,salary, commission*num_sales) AS
TotalSalary
FROM wages;
2. Save your changes and comment out the query
3. We can take this one step further and cast the TotalSalary as a
decimal value and sort everything by the TotalSalary
Modify the query to match the example shown below:
4. Execute the query, save your changes and comment out the query
1. Enter the following query:
USE Examples;
SELECT
emp_id, ISNULL(hourly_wage,0.00) AS Hourly, ISNULL(commission,0.00) AS
Commission, ISNULL(salary,0.00) AS Salary
FROM Wages;
2. In the result set, you will notice that the trailing zeros are
omitted. To make them display, we need to place the ISNULL function
inside the CAST function
Example: CAST(ISNULL(hourly_wage,0.00) AS
Decimal(10,2)) AS Hourly
Enter the revised query shown below:
3. Save
your changes and comment out existing queries
1. First we will run the query without any modifications
USE AP;
SELECT VendorState, COUNT(*) AS QtyVendors
FROM Vendors
GROUP BY VendorState WITH ROLLUP;
2. You will notice at the bottom of the data, it has a total of 122 with a heading of NULL next to it.
3. We can use the CASE function to display State Total instead of NULL
4. Modify the query shown below to display State Total instead of NULL.
USE
AP;
SELECT CASE
WHEN GROUPING(VendorState) = 1 THEN 'State Total'
ELSE VendorState
END AS VendorState,
COUNT(*) AS QtyVendors
FROM Vendors
GROUP BY VendorState WITH ROLLUP
5. Save your changes and comment out the query